Table of Contents
As more and more applications are deployed on cloud systems and cloud systems are growing in complexity, managing the cloud infrastructure is becoming increasingly difficult. SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring helps mastering this challenge by providing a sophisticated Monitoring as a Service solution that is operated on top of OpenStack-based cloud computing platforms.
The component architecture of OpenStack provides for high flexibility, yet it increases the burden of system operation because multiple services must be handled. SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring offers an integrated view of all services and assembles and presents related metrics and log data in one convenient access point. While being flexible and scalable to instantly reflect changes in the OpenStack platform, SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring provides the ways and means required to ensure multi-tenancy, high availability, and data security.
SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring covers all aspects of a Monitoring as a Service solution:
-
Central management of monitoring and log data from medium and large-size OpenStack deployments.
-
Storage of metrics and log data in a resilient way.
-
Multi-tenancy architecture to ensure the secure isolation of metrics and log data.
-
Horizontal and vertical scalability to support constantly evolving cloud infrastructures. When physical and virtual servers are scaled up or down to varying loads, the monitoring and log management solution can be adapted accordingly.
The basic usage scenario of setting up and using the monitoring features of SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring looks as follows:
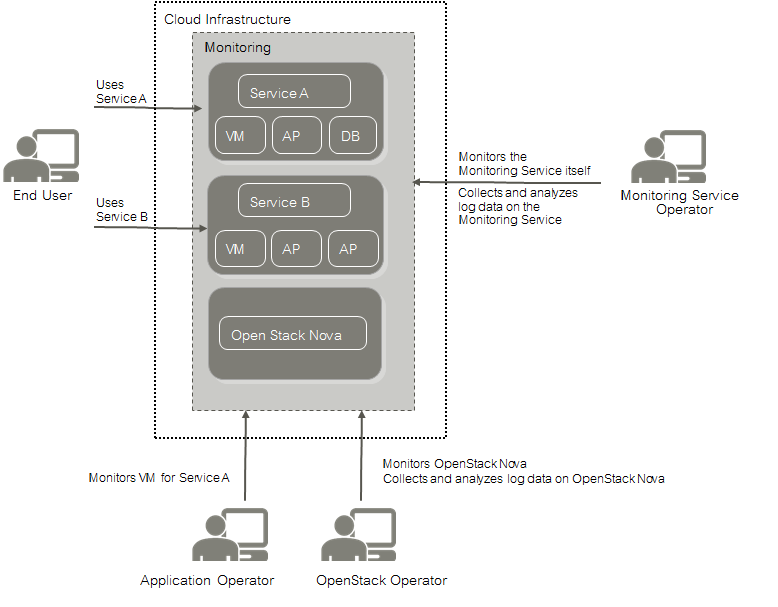
An application operator acts as a service provider in the OpenStack environment. He books virtual machines to provide services to end users or to host services that he needs for his own development activities. SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring helps application operators ensure that their services and the servers on which they are provided are configured and working as required.
The OpenStack operator is a special application operator who is responsible for administrating and maintaining the underlying OpenStack platform. The monitoring and log management services of SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring enable him to ensure the availability and quality of the platform. He uses SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring for:
-
Monitoring physical and virtual servers, hypervisors, and OpenStack services.
-
Monitoring middleware components, for example, database services.
-
Retrieving and analyzing the log data of the OpenStack services and servers, the middleware components, and the operating system.
As the Monitoring Service operator, you are responsible for providing the monitoring and log management features to the application operators and the OpenStack operator. This enables the application operators and the OpenStack operator to focus on operation and the quality of their services and servers without having to carry out the tedious tasks implied by setting up and administrating their own monitoring software. You use the monitoring features yourself for ensuring the quality of SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring.
The Monitoring Service Operator's Tasks
As the Monitoring Service operator, you have the following responsibilities:
-
Deploying the Monitoring Service, thus providing the monitoring features to the application operators, and the monitoring and log management features to the OpenStack operator.
-
Regular maintenance of the components and services SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring consists of.
-
Backup of the SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring databases, configuration files, and customized dashboards.
-
Monitoring of SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring to ensure the SUSE OpenStack Cloud Monitoring quality. For monitoring, you use a graphical user interface that is seamlessly integrated into the cloud infrastructure. Based on OpenStack Horizon, the user interface visualizes the health and status of your cloud resources and enables user access to all monitoring and log management functionality.
The tasks of the Monitoring Service operator and the OpenStack Operator can jointly be performed by one system operator. In this case, also refer to the OpenStack Operator's Guide.